JUMP Pedagogy
The JUMP123 pedagogy offers a structured and effective way to teach programming, breaking down the learning process into manageable steps that align with how students best absorb and retain information.
Creating effective programming lessons with JUMP123
Teaching programming in computer science presents a unique set of challenges, particularly when it comes to balancing the introduction of technical skills with keeping students fully engaged. The JUMP123 pedagogy offers a robust and systematic approach to teaching programming, breaking down the learning process into digestible steps that align with how students naturally absorb and retain information most effectively.

Working memory and long-term memory
Working memory serves as our short-term memory reservoir, where we temporarily store new knowledge or skills while learning. In contrast, long-term memory is where information is stored for extended periods, allowing us to recall it weeks, months, or even years later. The real challenge lies in transferring information from working memory to long-term memory, a process significantly impacted by cognitive load.
Cognitive load
Cognitive load refers to the amount of new information our working memory can handle at any given time. When this capacity is exceeded, students struggle to retain new information, which hampers their ability to grasp and apply programming concepts. Effectively managing and reducing cognitive load can dramatically improve retention rates and facilitate deeper learning in programming education.
The semantic wave
The semantic wave technique offers a powerful method for teaching complex topics by guiding students from abstract, challenging concepts to more tangible, relatable ideas, and then back up to the technical level. This approach is particularly advantageous in programming lessons, where students must grasp both theoretical concepts and technical language to succeed.
Focus on what is essential
When implementing the JUMP pedagogy, it’s crucial to prioritize the most important learning objectives and defer less critical areas to avoid overwhelming students. The core content is then divided into chapters, with each lesson comprising several chapters. To be truly effective, each chapter must complete its own semantic wave, ensuring that information is successfully transferred from working memory to long-term memory.
Use JUMP activities to embed programming skills and knowledge
JUMP activities are instrumental in helping students navigate the semantic wave within each lesson. These activities can be tailored and sequenced to suit the specific learning task at hand. JUMP stands for Judge, Unpack, Modify, and Program, with the first two elements focused on reinforcing theoretical understanding and the latter two honing practical programming skills.
Practical programming is key
Incorporating ample practice time is crucial for helping students transfer newly acquired skills from working memory to long-term memory. This ensures that these skills are deeply embedded and can be recalled later to solve new problems. By reinforcing learning through repetition, students make consistent progress, reducing the need for re-teaching and minimizing frustration for both teachers and students alike.

Download an entire free lesson
Grab your copy of a free Python lesson to see JUMP123 pedagogy and assessment methodology for yourself.
Download your FREE guide
Grab your copy of the free quick guide to JUMP123 which includes the JUMP pedagogy and the 123 assessment method below:
Buy ready to use teaching resources
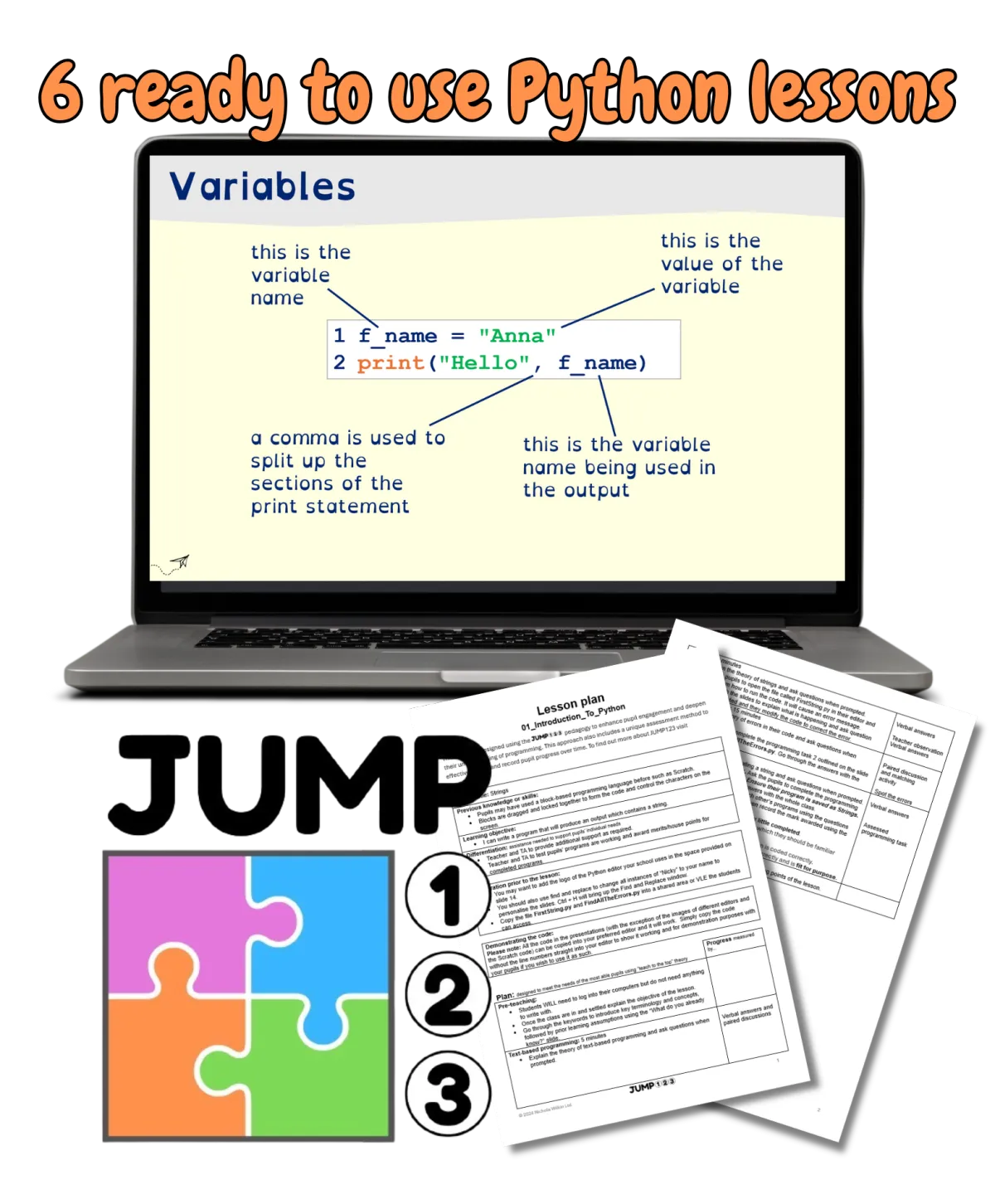
This set of 12 fully editable lessons uses the JUMP123 methodology, designed to make Python lessons both interactive and effective. The structure, based on proven educational psychology, reduces cognitive load for students, helping them master Python more efficiently.
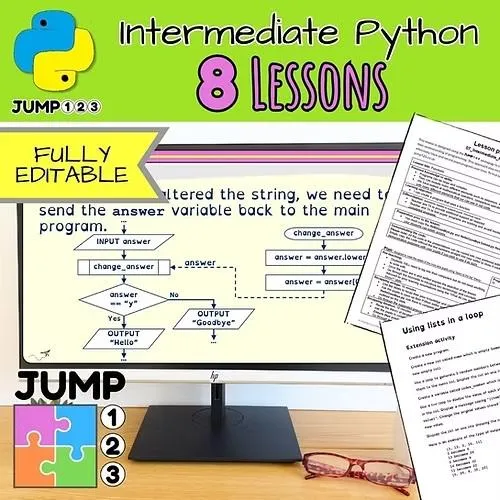
This dynamic intermediate Python unit includes 8 ready-to-use lessons and builds on the skills learnt in the Introduction to Python unit. It focusses more on empowering students to become more confident, capable programmers with enhanced problem-solving abilities.
FREE DOWNLOAD
Transform Your Python Teaching: Get 6 FREE JUMP123 Lessons Today!
Revolutionise the way you teach Python programming with these 6 complete JUMP123 lessons.
Designed to simplify complex concepts and captivate your students, they will save hours of preparation time.
Subscribe now and unlock your free resources – because teaching should be inspiring, not exhausting!